

Based on running dynamics analysis technology, we provide 12 running metrics for real-time foot tracking to help runners assess their running form, reduce the risk of injury, and improve running efficiency.
Duration
Steps (steps)
Distance (km)
pace (min'sec
Cadence (steps/min, spm)
Stride (cm)
Ground contact time (GCT, ms)
Flight time (ms)
Stance time to flight time ratio
Eversion (degree)
Foot strike patern (%)
Landing Impact (BW)
The duration of time between the user turning on and ending the exercise mode.
The cumulative number of times the user moved his feet alternately during the exercise period.
The total distance (km) accumulated by the user during the exercise.
It reflects how fast or slow the user walks or runs and how long it takes to complete a given distance (m's''/km).
The number of steps per minute (in steps/minute) that a user takes when walking or running.
The length of each stride the user takes when walking or running, i.e. the distance between the centers of the feet (cm).
The average duration of time between landing and leaving the ground with one foot when the user is running.
Ground contact time is related to speed, cadence, and running efficiency, the shorter the ground contact time represents the high efficiency of muscle elastic energy conversion, the higher the running efficiency. Generally, the elite runners usually have a ground contact time of 220 milliseconds or less.
During running, please pay attention to whether you have problems such as heel landing first, straddle running and pushing stirrups, and consciously use your forefoot on the ground and speed up the cadence to adjust the running posture, improving training effect.
It refers to the time neither foot is in contact with the ground between consecutive steps of the left to the right foot or vice versa.The flight time of excellent runners is generally greater than 125 milliseconds.
Ground contact time/flight time. Under the same cadence, a smaller stance time to flight time ratio indicates better running skills, and there is more time spend in the air. (with no ground contact)
The lighter and smoother the running posture, the more efficient the running. In general, the stance time to flight time ratio of elite marathon runners is about 1.0, elite sprinters about 0.5, and ordinary runners about 2.0.
Strengthening the runner's forward-leaning upward pulling technique training can improve the stride length, increase the stance time to flight time ratio, reduce stance time to flight time ratio and further improve the running efficiency.
It is more effective and easier to do for ordinary runners. See the advice on how to reduce ground contact time.
The eversion degree refers to the angle at which the ankle rotates inward from the initial landing to the start of the stirrups when the user is running. with the help of foot eversion, users can cushion ground forces and reduce the vibration.
The normal range of ankle rotation is usually between 5° and 25°. If the angle of foot rotation is too small (less than 5°), the muscle cushioning will be weakened, which will easily lead to plantar pain, calf pain, knee injuries, or other problems.
On the other hand, if the angle of pronation is too large (greater than 25°), it can lead to ankle ligament strains. Studies have found that running injuries occur least when the eversion angle is between 7-10 degrees.
The user walks or runs with a single-foot landing to contact the ground instantly.
There are three main foot strike patterns: forefoot landing, full-foot landing, and heel landing.
Forefoot landing
It means landing on the forefoot firstly, followed by the heel, to keep the weight of the body on the forefoot when users are running. This method is suitable for elite runners such as sprinters, long-distance runners.
Full-foot landing
It is a landing way that between the forefoot and the heel landing. The full-foot landing is not the entire foot landing at the same time, but actually the outside of the foot lands first, and quickly transitions to the inside of the full-foot landing.
Heel landing
It means the heel first lands on the ground and then transition to the forefoot, completing a gait cycle by internally rotating and stomping the ground during running,. Although heel landings have a high landing impact on the knee joint, most runners are used to landing on their heels. The user can adopt special training to improve it.
It refers to the maximum value of the ground reaction force on the pelma when the user touches the ground during running.
The better the cushioning technology, the smaller the landing impact; Meanwhile, running pace and landing impact usually show a positive correlation, the faster the speed, the greater the landing impact. The unit of landing impact is usually expressed as a multiple of body weight (BW, Body Weight). For example, 2.5BW means that the maximum value of ground reaction force on the pelma is 2.5 times of body weight during the running process.

The user can start the running analysis mode on device or mobile APP.

The user can check 12 metrics of data during running in real time, such as cadence, stride, landing Impact and foot strike patter, helping to adjust the running form at any time and improve the running efficiency.

After running, the user can check all the professional running data and the definition, to master and improve the running form timely.
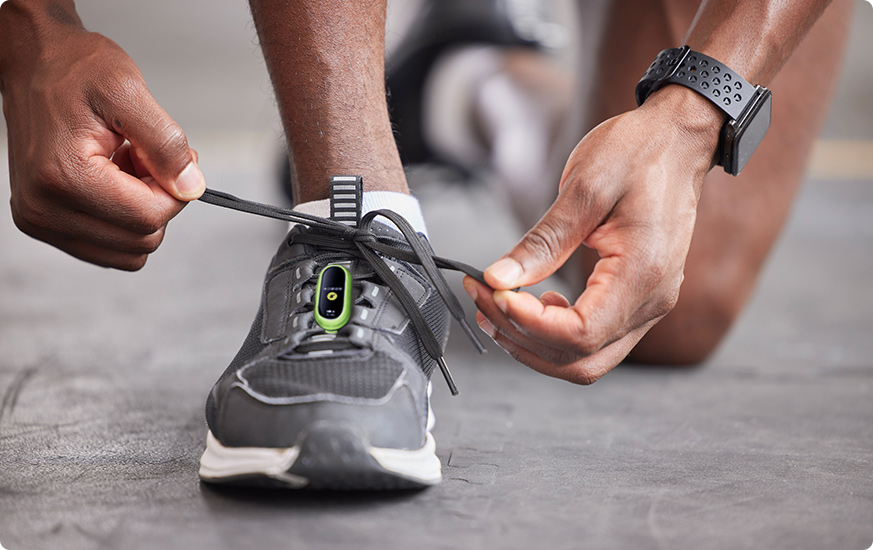

The user can start the running analysis mode on device or mobile APP.
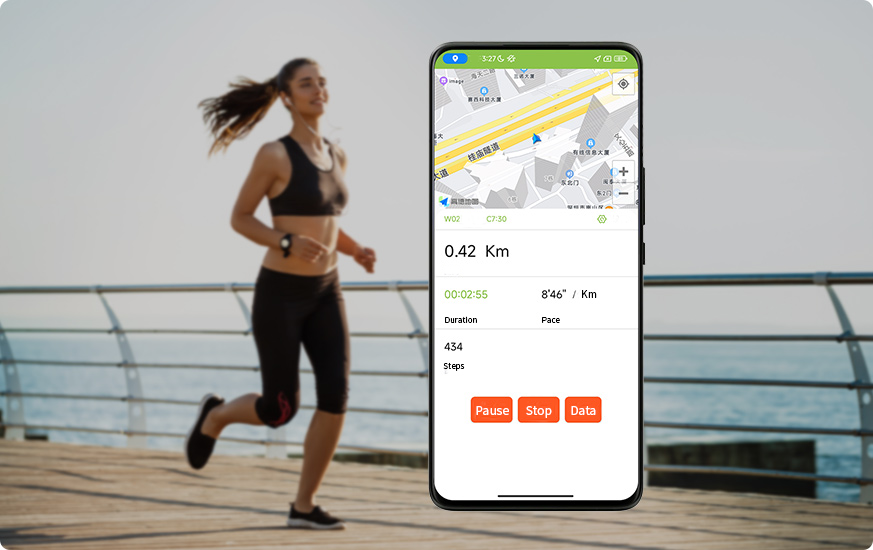
The user can check 12 metrics of data during running in real time, such as cadence, stride, landing Impact and foot strike patter, helping to adjust the running form at any time and improve the running efficiency.
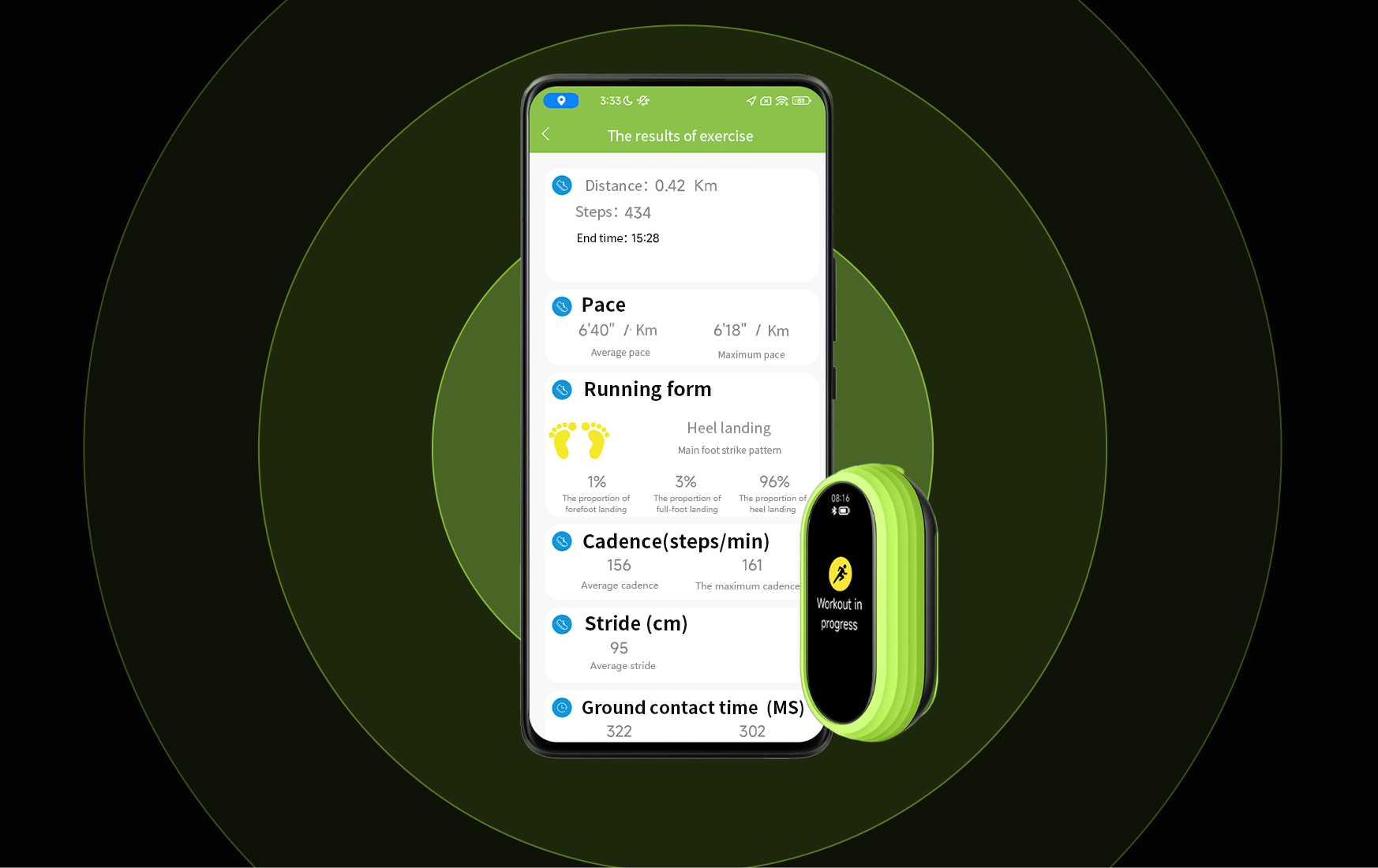
After running, the user can check all the professional running data and the definition, to master and improve the running form timely.